Joseph C. Maroon, MD, FACS is clinical professor and vice chairman of the Department of Neurological Surgery and Heindl Scholar in Neuroscience at the University of Pittsburgh Medical Center. In addition to being a renowned neurosurgeon, he is a sports medicine expert, health and nutrition expert and Ironman triathlete.
 Dr. Maroon, the neurosurgeon
Dr. Maroon, the neurosurgeon
Dr. Maroon is regarded as a premiere specialist in the surgical treatment of injuries and diseases of the brain and spine, specializing in minimally invasive procedures. Consistently listed in America’s Best Doctors for the past 20 years, he has an international referral base, including numerous professional athletes and celebrities.
Dr. Maroon obtained his medical and neurosurgical training at Indiana University, Georgetown University, Oxford University in England and the University of Vermont. He conducted extensive research into neurotrauma, brain tumors and diseases of the spine, which has led to many innovative techniques for diagnosing and treating these disorders. His research efforts garnered him numerous awards from various national and international neurological societies.
Dr. Maroon is the author of six books, and (co-)author of 40 book chapters and over 270 published scientific papers. He has given more than 150 presentations at national and international conferences and is often invited as visiting professor and key-note speaker. He has served on the editorial boards of eight medical and neurological journals and is currently associate editor of Surgical Neurology, and editorial board member of Neurological Research and The Physician and Sports Medicine journals. He also is past-President of the Congress of Neurological Surgeons, the largest society of Neurosurgeons in the world.
 Dr. Maroon, the sports medicine expert
Dr. Maroon, the sports medicine expert
Dr. Maroon has been the team neurosurgeon for the Pittsburgh Steelers since 1981, and is Medical Director of the World Wrestling Entertainment (WWE). He has successfully performed surgery on numerous professional football players and other elite athletes with potentially career-ending neck and spine injuries. Notably, he safely returned most to their high level of athletic performance.
Dr. Maroon is highly invested in the prevention and treatment of concussions in high school, college and professional sports, specifically football. While working with the Steelers in the early 1990’s, the lack of an objective, reliable instrument to evaluate concussion symptoms became very apparent to Dr. Maroon. To fill this void, he and Dr. Mark Lovell developed ImPACT™ (Immediate Post-Concussion Assessment and Cognitive Testing), an easy-to-administer, 20 minute long test to assess presence and severity of concussion symptoms. ImPACT™ has become the world-wide standard tool to assess sports-related concussions, and has been used in over 23 million athletes (as of 2022). In 1994, Dr. Maroon joined the National Football League’s mild Traumatic Brain Injury Committee as concussion expert. This committee, which in 2007 was renamed National Football League’s Head, Neck and Spine Committee, is still in place.
For his expertise on sports medicine and concussions, Dr. Maroon is frequently interviewed and quoted by the media, including the New York Times, USA Today, Associated Press, ESPN, Sports Illustrated, and ABC News Nightline.
 Dr. Maroon, the health and nutrition expert
Dr. Maroon, the health and nutrition expert
Dr. Joseph Maroon has a major interest in regenerative medicine and is senior Vice-President of the American Academy of Anti-Aging Medicine. Furthermore, he is on the Board of Directors of Mylan Laboratories, the 3rd largest Generic drug company in the world and is Chairman of their Science and Technology Committee. Dr. Maroon is also Chairman of the Medical advisory board of General Nutrition Centers (GNC).
Dr. Maroon developed research interests in the use of omega-3 fatty acids as a safe and natural alternative to non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) in treating neck and low-back pain in patients with disc and arthritic causes. He wrote the book, Fish Oil: The Natural Anti-Inflammatory, which highlights many of the benefits of fish oil, not just for back-pain, but also for general good health.
His recent research interests involve the dietary supplement resveratrol, found in red grape skins, which has been shown to activate genes for improved health. To make his research findings available to the public, he authored the book, The Longevity Factor: How Resveratrol and Red Wine Activate Genes for a longer and Healthier Life. In 2012, this book was made into a PBS special and featured in TV stations throughout the country.
Through his intensive athletic involvement, Dr. Maroon has a personal interest in healthy living and healthy nutrition. He is much invested in keeping his expertise up to date as he “practices what he preaches”.
Dr. Maroon, the athlete
 Dr. Maroon received an athletic scholarship to Indiana University in Bloomington, Indiana where as an undergraduate, he was named a Scholastic All-American in football. Dr. Maroon has successfully maintained his personal athletic interests through participation in 9 marathons and more than 72 Olympic-distance triathlon events. However, his greatest athletic accomplishment is his participation in 8 Ironman triathlons (Hawaii – 1993, 2003, 2008, 2010, 2013; Canada – 1995; New Zealand – 1997; Germany – 2000), where he usually finishes in the top 10 of his age group. Recently, in July 2012 and 2013, he finished second and third, respectively, in his age group in the Muncie, Indiana half Ironman triathlon. In October 2013 he completed his 5th World Championship Ironman in Kona, Hawaii.
Dr. Maroon received an athletic scholarship to Indiana University in Bloomington, Indiana where as an undergraduate, he was named a Scholastic All-American in football. Dr. Maroon has successfully maintained his personal athletic interests through participation in 9 marathons and more than 72 Olympic-distance triathlon events. However, his greatest athletic accomplishment is his participation in 8 Ironman triathlons (Hawaii – 1993, 2003, 2008, 2010, 2013; Canada – 1995; New Zealand – 1997; Germany – 2000), where he usually finishes in the top 10 of his age group. Recently, in July 2012 and 2013, he finished second and third, respectively, in his age group in the Muncie, Indiana half Ironman triathlon. In October 2013 he completed his 5th World Championship Ironman in Kona, Hawaii.
As a result of his athletic dedication and performance, Dr. Maroon (along with NFL’s great Joe Montana and NBA legend Kareem Abdul-Jabbar) was inducted into the Lou Holtz Upper Ohio Valley Hall of Fame for his athletic accomplishments and contributions to sports medicine on June 27, 1999. Eleven years later, on March 14, 2010 he was inducted into the National Fitness Hall of Fame in Chicago. Other inductees include Gov. Arnold Schwarzenegger; Jack LaLanne; and Kenneth Cooper, founder of the Aerobic Movement.
For all his accomplishments, Dr. Maroon was in 2011 selected as a “Distinguished Alumnus” of Indiana University—one of 5 selected annually from 500,000 alumni from the university.
Disclaimer
Tri-State Neurosurgical Associates-UPMC
Administrative Oakland Office Address:
Presbyterian University Hospital
Department of Neurosurgery
Suite 5C
200 Lothrop Street
Pittsburgh, PA 15213
Phone: 1-888-234-4357
© 2013 Tri-State Neurosurgical Associates – UPMC
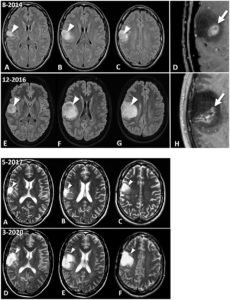 Current Case Report:
Current Case Report:



 Dr. Maroon received an athletic scholarship to Indiana University in Bloomington, Indiana where as an undergraduate, he was named a Scholastic All-American in football. Dr. Maroon has successfully maintained his personal athletic interests through participation in 9 marathons and more than 72 Olympic-distance triathlon events. However, his greatest athletic accomplishment is his participation in 8 Ironman triathlons (Hawaii – 1993, 2003, 2008, 2010, 2013; Canada – 1995; New Zealand – 1997; Germany – 2000), where he usually finishes in the top 10 of his age group. Recently, in July 2012 and 2013, he finished second and third, respectively, in his age group in the Muncie, Indiana half Ironman triathlon. In October 2013 he completed his 5th World Championship Ironman in Kona, Hawaii.
Dr. Maroon received an athletic scholarship to Indiana University in Bloomington, Indiana where as an undergraduate, he was named a Scholastic All-American in football. Dr. Maroon has successfully maintained his personal athletic interests through participation in 9 marathons and more than 72 Olympic-distance triathlon events. However, his greatest athletic accomplishment is his participation in 8 Ironman triathlons (Hawaii – 1993, 2003, 2008, 2010, 2013; Canada – 1995; New Zealand – 1997; Germany – 2000), where he usually finishes in the top 10 of his age group. Recently, in July 2012 and 2013, he finished second and third, respectively, in his age group in the Muncie, Indiana half Ironman triathlon. In October 2013 he completed his 5th World Championship Ironman in Kona, Hawaii.