Understanding Human Longevity: Why Humans Will Continue to Live Longer
 Human society has evolved at such a dramatic rate over the last 10,000 years that despite a similar facial appearance if we did somehow meet an early ancestor few would recognize any significant similarities. Early man was generally short, hungry, unkempt by today’s standards and most often didn’t live past the age of 30. As a society in the last 200 years we have dramatically improved the human condition and associated human longevity through a more stable food source, immunizations and anti-infection methods and medications. As a result many people of the world will live well into their late 70’s and early 80’s in generally good health. At this point in our human timeline we are now at a cross roads of many competing influences that will either potentially continue this trend towards increased longevity for some or potentially reverse it for others.
Human society has evolved at such a dramatic rate over the last 10,000 years that despite a similar facial appearance if we did somehow meet an early ancestor few would recognize any significant similarities. Early man was generally short, hungry, unkempt by today’s standards and most often didn’t live past the age of 30. As a society in the last 200 years we have dramatically improved the human condition and associated human longevity through a more stable food source, immunizations and anti-infection methods and medications. As a result many people of the world will live well into their late 70’s and early 80’s in generally good health. At this point in our human timeline we are now at a cross roads of many competing influences that will either potentially continue this trend towards increased longevity for some or potentially reverse it for others.
Every moment of every day the body is rebuilding itself to survive and thereby increase our longevity. This is done daily through billions of cellular divisions. In fact about 1% of our cells are made new each day. Entire organ systems in our bodies can be completely replaced in 6 months time. Our cells have a unique blueprint developed through the millennium that tells our body how to create new cells. But our decisions as to how or if we exercise, what we eat or don’t eat and to what type of environment we are exposed to has a direct influence on whether live prolonging or life limiting qualities are activated in each cell that is created. Our choices have the ability to either help or hurt this biological process which ultimately affects our lifespan.
Epigenetic Activation – The Power to Live Longer
The actions on the body of physical activity, food quality and quantity and environmental exposures were believed to work generally on either specific organ systems of our body or in the cellular protoplasm providing energy sources or toxins to be disposed of. Research now proves the most profound effects on our bodies from these outside sources actually occur within our cellular nucleus in our genes, the blueprints of life.
What we have often been told and many believe is that our fate or longevity is irrevocably linked to our parents. If a man and your father died at 60, as you approach your 60th year, there is a natural anxiety that you also have reached your “genetic time limit” and beyond this you are on “borrowed time”. This apprehension can often made worse if certain diseases, such as heart attack or stroke, were the cause of your parent’s death. We can’t escape our parent’s genes for heart disease, we are told so often, why try to live a healthier life. But what if you were told that in general your existing genetic code only accounts for 30% of your overall longevity or lifespan and that up to 70% is under your control.
This fact, “the 30/70 rule”, requires the understanding of a whole new field of science that is just now beginning to explain how or if we exercise, what we eat and to what type of environment we are exposed to has a direct influence on whether health producing or health limiting genes are activated in each cell of our body. Our genetic code for either a positive effect (increased health and longevity) or for a negative effect (poor health and premature death) is linked more to factors we can influence than those inherited from our parents.
This new discovery must be linked back to the famous discovery by Watson and Crick in 1953, DNA. Deoxyribonucleic acid forms the basic double helix structure that can hold the complexity of all life on earth on just 23 pairs of chromosomes housed in the cell nucleus of every cell in the human body. Its most basic description can be referred to as a blueprint. When building any structure, in the case of a human cell perhaps a protein, the DNA blueprint is mostly a passive structure. It requires other cell structures and molecules called transcription factors to read the DNA blueprint and then in turn to construct the protein building blocks, amino acids, in to their proper configuration. These other structures, that do the actual construction, can be influenced to read only certain sections of the DNA blueprint or even to misread and place wrong sections of proteins together. The complexity of DNA blueprint reading and those things that can influence the proper reading to make those items that we need our cells for is the new science of Epigenetics.
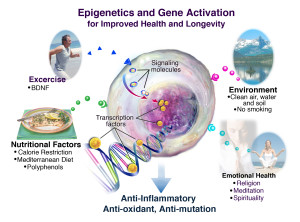
Copyright 2009 -Joseph C. Maroon, MD
The above picture helps to demonstrate the concept of epigenetic influences from outside the cell sources (exercise, nutrition, environment and emotion) that can activate nuclear transcription factors that can result in either very healthy (ant-inflammatory, anti-oxidant, anti-mutation) or unhealthy conditions being propagated from DNA codes.
Using the science of epigenetics we now are able to explore and understand how factors such as exercise, diet, environment and emotion can have profound effects on our health and eventual life span. (see Drawing) What has been only recently discovered is that these listed factors can act to alter and influence many human epigenetic mechanisms that control how our genetic code is used or misused. Therefore the DNA blueprint, as provided by our parents and all our distant ancestors from the beginnings of life on earth, can exist and yet not all aspects of that code will necessarily be expressed due to the actions of epigenetic factors.
One of the best ways to explain this concept is by an example of a discovery by scientists Lenny Guarente at MIT and David Sinclair at HarvardMedicalSchool. In the late 1990’s using yeast cells, they discovered that by stressing theses cells with less sugar than they normally consumed (caloric restriction) they found that many of the cells lived up to 60% longer than typical cells. This discovery was not itself new but what happen next was. Guarente and Sinclair discovery there was a protein enzyme called Sir2 (silent information regulation 2), or know by its family name as Sirtuins, in yeasts that once activated caused their DNA structure to curl up tighter and allow for a more efficient cellular division. By doing this sirtuins allowed the yeast to divide for a longer period and thus live longer. What the caloric restriction stress did, through the action of a Sirtuin enzyme, was to read just the section of DNA blueprint code that produce additional DNA stabilizing proteins that ultimately allowed the yeast to live longer.
Since this discovery all animals, including humans, have been found to possess these Sirtuin activators. DNA stabilization by calorie restriction is just one pathway within animal cells that have been found to be activated from influences outside the cell nucleus itself which can control what sections of the DNA blueprint are read. We now know that many nutritional, activity and environmental factors can act on the DNA, in the same epigenetic manner, to produce very healthful and life prolonging actions. Guarente and Sinclair referred to these genes that become activated, and their life prolonging actions as “survival genes”, which describes the unique occurrence that is associated with calorie restriction stress and its metabolic life prolonging effect.
The function of sirtuins to improve cellular division may have a profound impact on cancer and longevity itself by preserving cellular structures. Certain nutritional, activity and environmental factors, can act on other epigenetic pathways to produce very health pathways that can also lead to prolonged life or potentially other very harmful substances that can lead to disease and early death. Thus the choices are ours.
The most recent discovery related to the Sirtuin activation and health benefit story was also discovered by Sinclair and another researcher, Marie Lagouge, in France. In 2006 they found the molecule, resveratrol, from the skin of dark skinned grapes and other natural sources, could also activate Sirtuins through the epigenetic pathway and reduplicate the benefits seen with caloric restrictions by also activating survival genes.
Additional studies now show that other dietary supplements, vitamins, minerals, diet choices and exercise can epigenetically activate a protein that can influence brain cells to divide and produce new brain cells. Also environmental factors such as some pollutant can act epigenetically to stimulate cancer cell growth.
The New Human Paradigm in Longevity
To discuss a new paradigm in human longevity we must explore how diet choices, food quantity and types we now consume have been profoundly altered from the diets of our early hunter gatherer ancestors. Their diet which was essentially unchanged through millions of years of evolution resulted to a genetic match which modern man now only remotely follows in our own diet and food choices. The foods consumed almost exclusively by early man, such as fish and seafood, containing omega-3 EFA’s, and fruits, nuts and berries, containing high amounts of health promoting polyphenols, such as resveratrol found in colored fruit skins, all have been shown to epigenetically prevent disease and in animals prolong life.
Calorie restriction, practiced unintentionally by early man, has significant health benefits. Diets that consume high levels of omega-3’s, green teas and herb remedies such as polygonum capsicum (also a source of resveratrol) are also found to improved longevity and health in modern cultures where these diets are common.
In summary, if the goal is to just live a few years longer than average then we are not interested in any serious dramatic health improvements. But to have a new paradigm in longevity we must both understand and practice health enhancing measures that work on an epigenetic, cellular level that works to prevent illness and not just to fight it once it occurs (sickcare). The idea of preventative medicine or “healthcare” must include choices that can lead to the best chances for a longer and healthier lifespan.



 Dr. Maroon received an athletic scholarship to Indiana University in Bloomington, Indiana where as an undergraduate, he was named a Scholastic All-American in football. Dr. Maroon has successfully maintained his personal athletic interests through participation in 9 marathons and more than 72 Olympic-distance triathlon events. However, his greatest athletic accomplishment is his participation in 8 Ironman triathlons (Hawaii – 1993, 2003, 2008, 2010, 2013; Canada – 1995; New Zealand – 1997; Germany – 2000), where he usually finishes in the top 10 of his age group. Recently, in July 2012 and 2013, he finished second and third, respectively, in his age group in the Muncie, Indiana half Ironman triathlon. In October 2013 he completed his 5th World Championship Ironman in Kona, Hawaii.
Dr. Maroon received an athletic scholarship to Indiana University in Bloomington, Indiana where as an undergraduate, he was named a Scholastic All-American in football. Dr. Maroon has successfully maintained his personal athletic interests through participation in 9 marathons and more than 72 Olympic-distance triathlon events. However, his greatest athletic accomplishment is his participation in 8 Ironman triathlons (Hawaii – 1993, 2003, 2008, 2010, 2013; Canada – 1995; New Zealand – 1997; Germany – 2000), where he usually finishes in the top 10 of his age group. Recently, in July 2012 and 2013, he finished second and third, respectively, in his age group in the Muncie, Indiana half Ironman triathlon. In October 2013 he completed his 5th World Championship Ironman in Kona, Hawaii.